|
|
Enceladus ("en SEL a dus") is the eighth of Saturn's known satellites:
orbit: 238,020 km from Saturn
diameter: 498 km
mass: 7.30e19 kg
In Greek mythology Enceladus was a Titan who was defeated in battle and buried under Mount Etna by Athena.
Discovered in 1789 by Herschel.
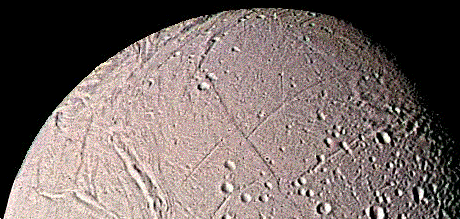
Enceladus
has the highest albedo
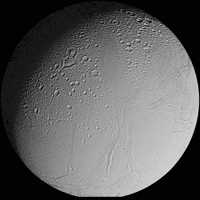 (>0.9) of any body in the solar system. Its surface is dominated
by fresh, clean ice.
(>0.9) of any body in the solar system. Its surface is dominated
by fresh, clean ice.
At least five different types of terrain have been identified on Enceladus. In addition to craters there are smooth plains and extensive linear cracks and ridges. At least some of the surface is relatively young, probably less than 100 million years.
This means that Enceladus must have been active until very recently (and perhaps is still active today). Perhaps some sort of "water volcanism" is at work.
Enceladus is much too small to still be heated by the decay of radioactive material in its interior (the heat would have all dissipated long ago).
Enceladus may be composed of some low-melting point material rather than pure water.
Enceladus may be the source of the material in Saturn's tenuous E ring. And since the material cannot persist in the ring for more than a few thousand years, it may be due to very recent activity on Enceladus. Another possibility, though, is that the rings are maintained by high-velocity collisions between dust particles and the various moons.