 - detritus, or litter on forest
floor
- detritus, or litter on forest
floor
A food web is a set of interconnected food chains by which energy and
materials circulate within an ecosystem.
The food web is divided into two broad categories: the grazing web, which typically begins with green plants, or algae, and the detrital web, which begins with organic debris (like the litter on a forest floor or the sea bed).
 - detritus, or litter on forest
floor
- detritus, or litter on forest
floorThese webs are made up of individual food chains.
In a grazing web, materials typically pass from plants to plant eaters (herbivores) to flesh eaters (carnivores).
In a detrital web, materials pass from plant and animal matter to bacteria and fungi (decomposers), then to detrital feeders (detritivores), and then to their predators (carnivores).
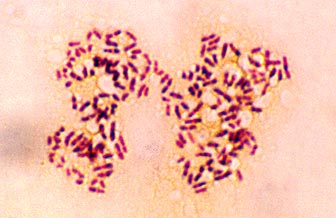
A detrivore (or detritus feeder) is an organism that eats the dead remains of other organisms (detritus). Examples of detrivores include some bacteria and fungi.
bacteria are too small to see with the naked eye
- 
Generally, many links exist within food webs. For example, the fungi that decompose matter in a detrital web may sprout mushrooms that are consumed by squirrels, mice, and deer in a grazing web.
Some birds are omnivores, that is, consumers of both plants and animals, and thus are in both detrital and grazing webs. The birds may typically feed on earthworms, which are detritivores that feed upon decaying leaves.