|
|
|
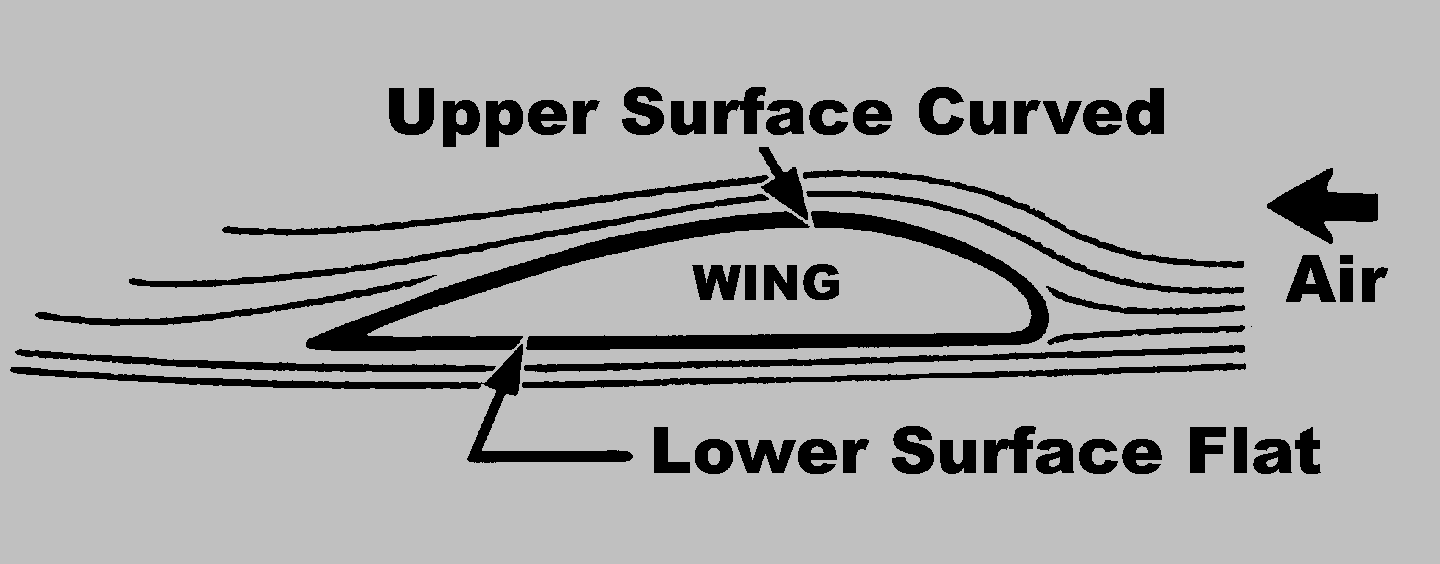
An airplane supports itself in flight by deflecting or bending the passing airstream downward.
The plane's wings push this airstream downward and the airstream reacts by pushing the wings upward.
This action/reaction effect is an example of Newton's third law of motion, which observes that forces always come in equal but oppositely directed pairs: if one object pushes on another, then the second object must push back on the first object with a force of equal strength pointing in the opposite direction.
Even air obeys this law so that when the plane's wings push air downward, the air must push the wings upward in response. In level flight, the deflected air pushes upward so hard that it supports the entire weight of the plane.
